2023-07-04 2628
1.1Essential information
Name: Sponge
Weight: 1kg
Variety: lop
Age: 1 year and 2 months
Sex: male without castration
1.2Injury situation
The rabbit fell from the upper floor (about 1 and 2 floors) in the morning. During the treatment, the hind limbs were paralyzed, the upper front teeth were broken, nasal bleeding, shortness of breath and poor appetite.
2.1Physical examination
The rabbit was in good spirits, short of breath and had broken upper incisors. Both hind limbs are unable to stand and have no autonomic movement ability. Neurological examination showed loss of proprioception in the left hindlimb, weakened right hindlimb, the knee-jerk reflex was decreased in both hindlimb, the retraction reflex was weakened in the left hindlimb, normal right hindlimb, and weakened bilateral muscle tone, especially in the left hindlimb. There is still bilateral deep hind limb pain, testing the cutaneous muscle reflex on both sides of the spine of the back, slightly weakened in the lumbar part.
2.2 Laboratory examination
The routine blood test showed normal red blood cells and no obvious anemia; normal leukocytes, but increased neutrophile granulocyte, decreased lymphocytes, and some stress leukocytes. Biochemical findings showed a mild increase in ALT, a large increase in AST, and a mild decrease in albumin, associated with muscle damage caused by falling buildings.
Routine blood test:
Project |
Result |
RRs |
Unit |
NEUT% |
74.8↑ |
14.0-62.0 |
% |
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV) |
60.22 |
59.0-70.1 |
fL |
White Blood Cell |
6.59 |
3.00-13.50 |
10^9/L |
MPV |
6.2 |
2.0-15 |
% |
RBC |
5.8742 |
4.5-6.9 |
10^12/L |
MPV |
5.7↓ |
6.5-12.0 |
fL |
PLT |
464 |
134-567 |
10^9/L |
Absolute Neutrophil Values |
4.93 |
0.50-6.60 |
10^9/L |
Mean Hemoglobin Concentration |
368↑ |
323-345 |
g/L |
Hematocrit |
35.3 |
313-43.34 |
% |
Erythrocyte Hemoglobin Distribution Width |
31↓ |
35-56 |
fL |
Percentage of Basophils |
3 |
0-8 |
% |
Mean Hemoglobin Content |
22.1 |
19.4-23.8 |
pg |
The Percentage of Lymphocytes |
15.6↓ |
25-824 |
% |
Platelet Distribution Width (PDW) |
15.64 |
9.0-17.0 |
fL |
Hemoglobin (HGB) |
130 |
110-1756 |
g/L |
Width (RDW-CV) |
12.1 |
11.0-16.0 |
% |
Absolute Value of Lymphocytes (LYMPH #) |
1.03 |
100-6.80 |
10^9/L |
Absolute Monocyte Value (MONO #) |
0.41 |
0.08-1.51 |
10^9/L |
Absolute Eosinophilia (EOS #) |
0.42 |
0-64 |
% |
Platelet Vocrit (PCT) |
0.266 |
0.108-0.282. |
% |
Alkoid Foot (BASO #) |
0.2 |
0.00-0.76: |
10^9 |
Eosinophils (EOS #) |
0.02 |
0.00-0.51 |
10^9/L |
Biochemistry :
Project |
Result |
RRs |
Unit |
Amylaceum (GLU) |
8.24 |
5.5-8.6 |
mmol/L |
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) |
75 |
40-150 |
U/L |
Usea Nitrogen (BUN) |
6.7 |
4.1-10.9 |
mmol/L |
Total Protein (TP) |
59 |
53-85 |
g/L |
K+(K+) |
5.2 |
3.5-6.2 |
mmol/L |
Total Bilirubin (TBIL) |
44 |
2-64 |
umol/L |
Globulins (GLOB) |
38 |
15-46 |
g/L |
Total Calcium (TCa) |
3.33 |
3.13-4.21 |
mmol/L |
Asparpartate Aminotransferase (AST) |
283↑ |
0-40 |
U/L |
Total Carbon Dio |
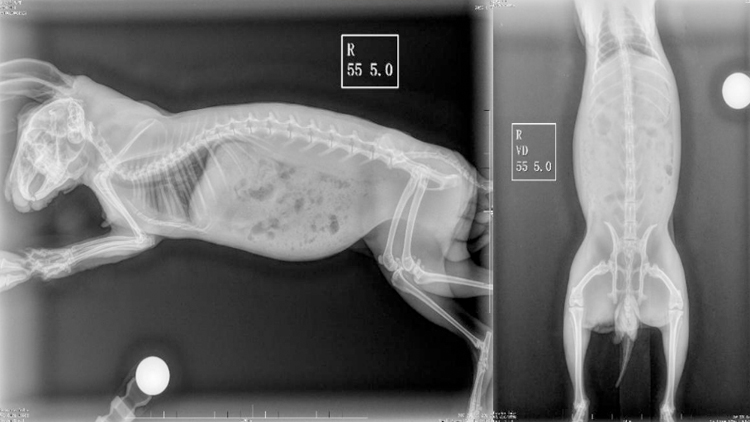
2.3 Imaging examination
The vertebral body in the figure showed complete structure with normal number, no fracture, dislocation / misalignment, inflammatory hyperplasia, and slight narrowing of the L4-L5 space. No fractures were found in the bones and the joints.
Based on the above examination, it is preliminarily judged that lumbar spinal cord injury caused by external force. At present, the injury caused by vertebral fracture can be excluded. However, whether there are any diseases such as disc herniation or myelitis requires further high-order imaging examination such as MRI to be confirmed.
In the early stage, the doctor of the different pet department communicated with the owner about the risk of MRI anesthesia and the postoperative operation plan. The owner decided to take conservative treatment first, so he was transferred to the physiotherapy department for treatment. Since the classification of paralysis in rabbits has not been reported or documented, the grading table of canine and cats was used. According to neurological examination, it can be graded as grade 4 paralysis. According to the literature, the effective rate of grade 4 paralysis can reach 80% to 90%. So laser and acupuncture was started twice a week.
Acupunture and moxibustion therapy
4.1 Laser physiotherapy
Preset scheme: exotic-musculoskeletal-lumbar-1000g
Treatment probe: 25mm zoom opening probe
Note: in the case of not picking hair should contact with the skin to do flat sweep, generally in the circle or S-shaped direction, do not stay in a part in the process of too long easy to cause skin burns.
4.2 Medication
Meloxicam oral solution, administered orally, 0.5mg / dose once a day for 5 days.
The injection solution was injected subcutaneously, 0.28ml / time, once a day.
4.3 Therapeutic process
4.3.1 Electroacupuncture + laser treatment, the rabbit's acceptance is also very high!
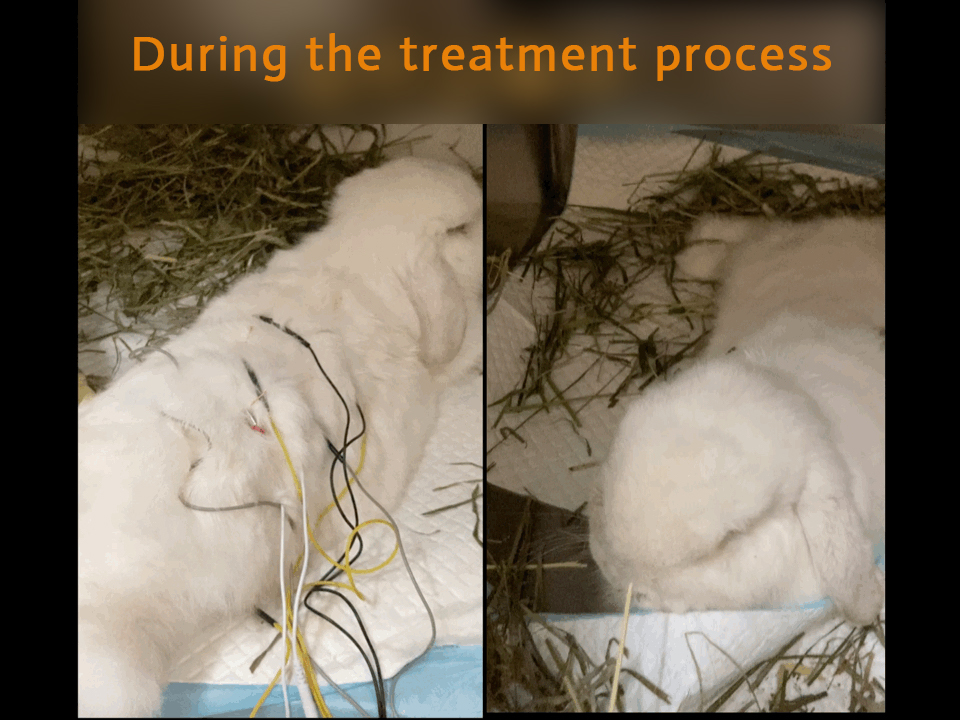
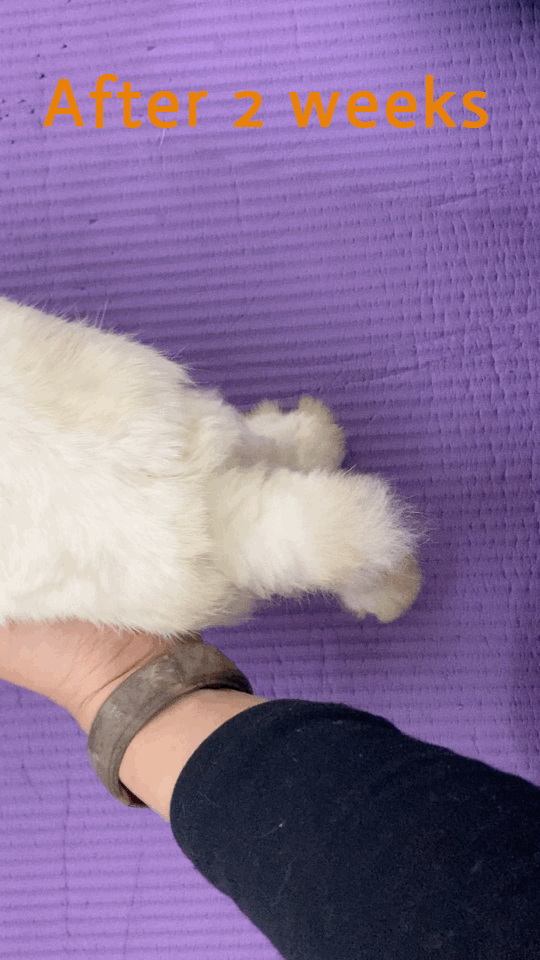
4.3.2 After two weeks, the pet can start walking at home, but can not jump. See body recovery in both hindlimbs, but the recovery is poor on the left.

4.3.3 A month later, the owner brought the pet for the last physiotherapy of the course, indicating that the pet's athletic ability has recovered and he can walk and jump.

Paralysis / paresis is common in rabbit disease, showing weakness or loss of neuromotor function, associated with neuromuscular joints, skeletal, spinal diseases, drug poisoning, systemic diseases or nutritional diseases. Its causes include fracture or dislocation of the lumbar spine, disc disease, fracture of the arch, brain protozoosis, toxoplasmosis, hypovitamin A, poisoning, nutritional diseases, tumors, osteoarthritis, etc.
A complete neurological examination is very helpful for the localization of the lesion and the differential diagnosis of the disease. The reflexes or reactions to be examined can be referred to dogs and cats, but it is worth noting that because rabbits belong to the bottom of the food chain and the innate natural protection mechanism, the results of neurological examination during stress may be unsatisfactory. According to the experience of the authors of the relevant literature, rabbits are more sensitive to posture changes and movement. For example, in spinal cord responses, both examination of ontology reaction and position reaction usually yield satisfactory results. The spinal reflexes were mainly used to distinguish upper and lower motor neurons and to determine lesion location. Different from dogs and cats, rabbits rarely bark or bite when checking the pain. They are good at hiding their pain, so it is more difficult for rabbits to evaluate the existence of pain, which brings some difficulties to determine the prognosis and the treatment plan of the disease. In this case, the absence of hindlimb ontological response suggested the impairment of nerve conduction function: the overall spinal cord of the hind limb low, and the forelimbs were normal, so it was judged to be a lesion of lower motor neurons, and the lesion was roughly located in the area from L 4 to S 4. Combined with the results of X-ray, spinal cord injury caused by fracture or dislocation was excluded, so spinal cord contusion and inflammation caused by intervertebral disc disease or caused by external force were suspected. However, due to the lack of further high-order imaging diagnosis, it was initially defined as spinal cord injury.
The treatment plan is mainly anti-inflammatory, analgesic and restoration of nerve function, and its purpose is to maintain the perfusion of the local injured tissue and reduce the inflammatory factors to reduce the secondary damage of the injured tissue. Since most secondary lesions will occur within 24 hours after injury, treatment should be started as early as possible. Analgesic drugs generally recommend non-steroidal or opioids.
Acupuncture with electric stimulation is one of the modern veterinary techniques, it is the use of electrical stimulation and acupuncture in clinical practice, it is recommended to use in nerve and bone diseases, it can effectively relieve pain and promote the recovery of nerve function.
Although scarce literature on rabbits, relevant literature has confirmed that electroacupuncture can play an analgesic effect in dogs and cats. It can stimulate the release of endorphin, an analgesic substances; reduce the release of local anti-inflammatory substances and histamine for anti-inflammatory effect; promote local microcirculation, effectively inhibit local tissue hypoxia, and promote tissue repair; and promote the regeneration of axons and damaged axons for regeneration of nerves.
As a non-invasive modern physiotherapy technique, the potential nerve repair function of laser therapy has been studied and reported. Related literature and animal experiments show that laser can promote SCI rat axonal regeneration and function, it by releasing anti-inflammatory factors such as TNF-α and IL-1?, inhibit the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and NF- κB activation, reduce inflammation, it can also activate transcription factors, enhance mitochondrial respiration, increase angiogenesis and nerve regeneration, to promote wound healing, tissue repair, reduce inflammation. It also prevents macrophages from gathering at the site of neuronal tissue injury, regulates the inflammatory process, and promotes the improvement of neuronal tissue repair by reducing the secretion of PEG 2 and LTB 4, thus reducing injury complications. A study by Goncalves and other experts showed that laser treatment after spinal cord injury can regulate the migration of immune cells in the spinal cord, reduce the inflammatory response in the spinal cord, and prevent the destruction of axonal myelination.The most important clinical feature affecting the outcome of SCI is still the degree of injury at the beginning of the onset. In order to judge the condition in more detail and objectively, we used a 5-point scale designed by lan Griffiths. According to most of the literature and case review, most level 1-4 recovery effect is more ideal, can reach 80% -90%, but for level 5, if in 24 hours (surgery, medicine, physiotherapy, etc.), the recovery rate will be greatly improved, in the first 3 months have 50-60% chance to recover, 10% in 18 months after spinal cord walking, but its autonomous urination function may not recover.
The rabbit level 4 paralysis caused by external force impact, belong to the acute injury of the spinal cord, the treatment in traditional Chinese medicine about 3-4 weeks (6-8 times) to restore nerve function, but he in the first 3-4 days after physiotherapy right leg (nerve loss is not serious) restored the normal ontology reaction, and muscle atrophy is mild. After 2 weeks of physiotherapy, the nerve function of the left and right legs was restored by about 80% (both hindlimb were restored, but the left hind leg was slightly weak), and they could walk, but could not jump. In the third week of physiotherapy (the 6th time), the basic motor function was restored, the walking was normal, and the hindlimb bounce force was restored. After 1 month, the nerve and motor function were basically recovered as before. His recovery cycle has actually exceeded expectations.
In the combined treatment of acupuncture and laser, laser has played a relatively large adjuvant treatment effect. Compared with electromagnetic wave and he-neon laser, high-energy laser instrument can illuminate deeper tissues, more effectively relieve local inflammatory reaction, reduce pain, promote the regeneration of nerve, and accelerate the recovery of nerve function. This case also reflects that besides dogs and cats, the same effect can be achieved for different pets.
Reference
Anna M, Brigitte L. BSAVA Manual of Rabbit Medicine[M]. British Small Animal Veterinary Association, 2014: 214-231.
Robert V; Linda J. N; Susan M.; Metabolic changes in rabbit spinal cord after trauma: Magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies[J]. 1989; 25(1), 26–31.
Saeed V, Mahnaz P.; A Review of Low-Level Laser Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury: Challenges And Safety[J]. Lasers Med Sci, 2020 Autumn; 11(4):363-368.
Wang Jin, Huang Lijun, Wang Ruixiao, Xu Rui, Brass, Wu Yanping, Liang Li, Chen Junfeng, Guo Tao. Effect of 650 nm low energy semiconductor laser on repair of full-thickness damage in rabbit ear skin [J]. Chinese Journal of Dermatology and Venereology, 2022,36 (02): 161-166.
Chen Shulin. Clinical study of He-Ne laser with acupuncture for the paralysis of thoracic and lumbar disc herniation in dogs [D]. Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2009.
Penderis J. Spinal cord injury in the dog: features of the neurological examination affecting prognosis[C]. Presented at 33rd Congress of World Small Animal Veterinary Association proceedings, Dublin, Ireland, August 20-24, 2008.