2023-07-10 2198
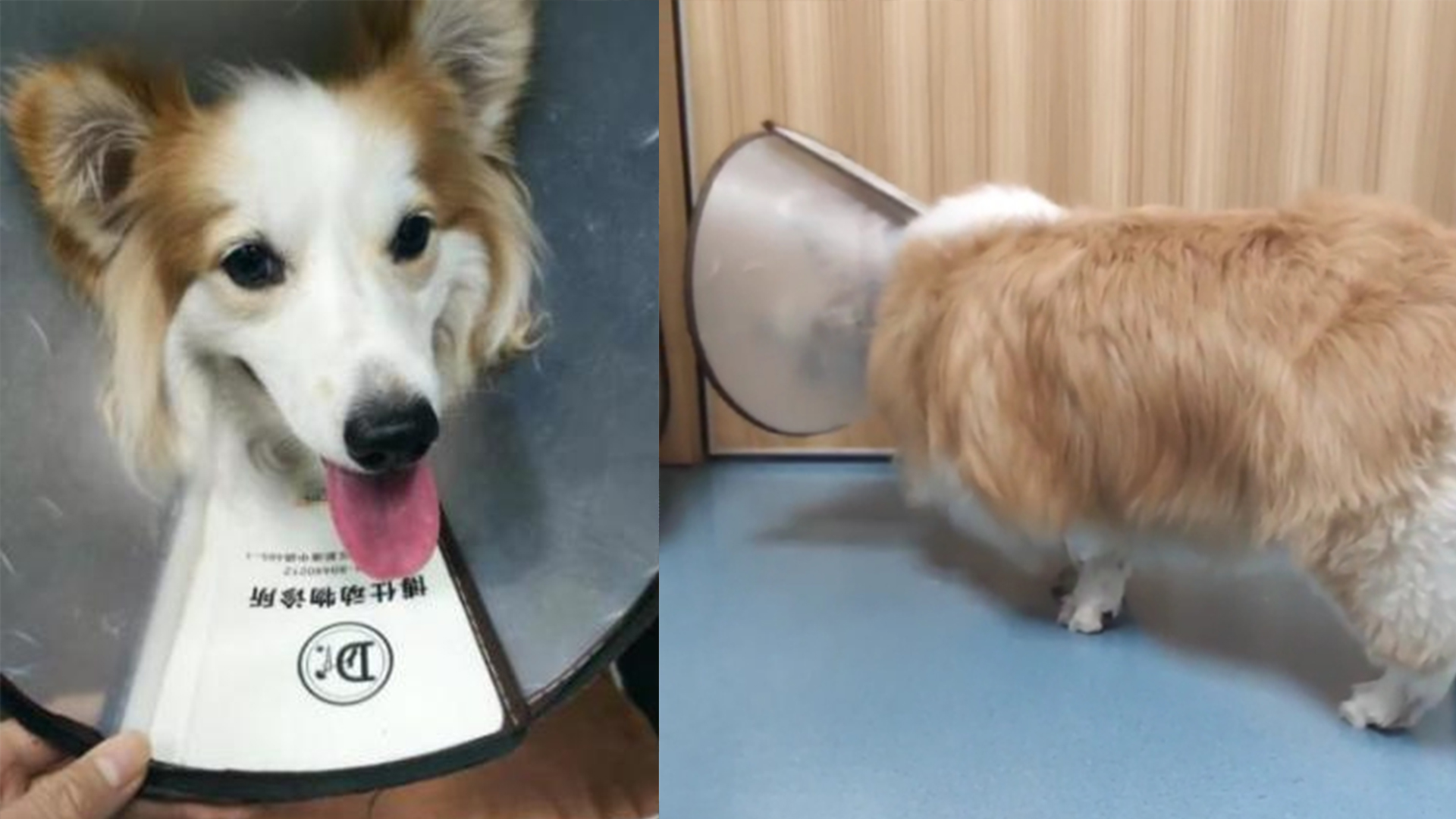
On April 8,2022, Guangzhou Boshi Animal Hospital received a corgi named JOJO. JOJO age 3 years 8 months, weight 16.2kg, gender female has been sterilized, gentle temperament. According to the owner of JOJO, the right hind limb was lame after playing with his partner yesterday. This is the second time that the right hind limb was lame. Dr. Wu Zhongheng asked the owner about the basic information and medical history of JOJO for the right hind limb palpation of JOJO. During palpation, the dog is nervous, so it is recommended to undergo ray examination and palpation after short-acting anesthesia. During the preparation period, the doctor recorded the dog walking before surgery, the limped in the right hind limb.
| Photos of JOJO at clinic visits | |
 |
 |
| Screenshot of palpation video | |
 | |
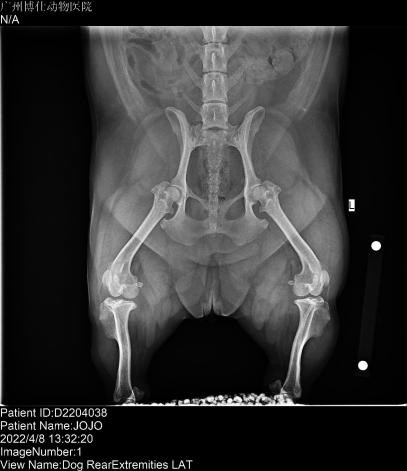
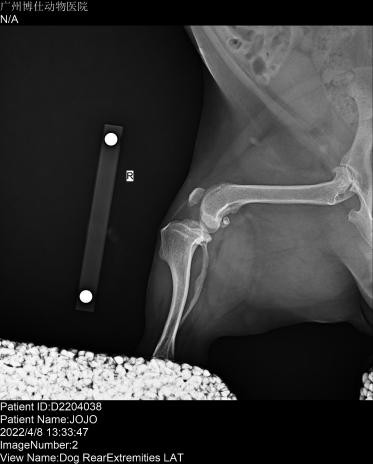
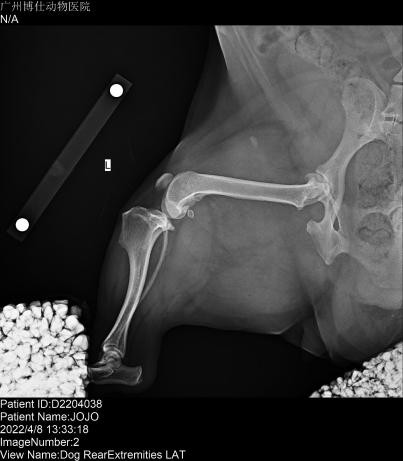
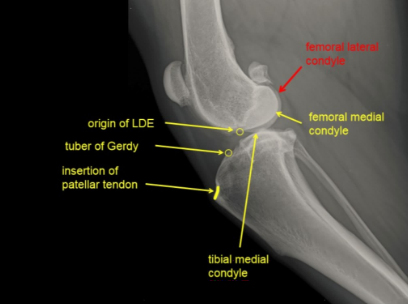
Short-acting anesthesia was administered with intravenous propofol at a dose of 8mg / kg. Put an indwelling needle, prepare endotracheal intubation to start anesthesia, and take bilateral knee position and open side. The X-ray showed a ruptured JOJO anterior cruciate ligament, positive drawer motion on palpation, movement of the popliteal fascia, and mild arthritis. No abnormalities were noted in the left hind limb.
| Pet X-ray inspection pictures | ||
 |
 |
 |
According to statistics, anterior cruciate ligament rupture is mostly 7-10 years old, about 34kg young dogs and about 26kg old dogs. Usually an acute anterior cruciate ligament rupture in pups or young dogs is associated with a meniscus injury. The odds of bilateral anterior cruciate ligament rupture within 8 – 12 months were greater than 30%, 94% had concurrent degenerative hip lesions, and 76 – 86% were asymptomatic.(Power,etal.javma#7 2005) Animals will increase the force of the anterior cruciate ligament during the knee joint, and the posterior cruciate ligament during extension, and their resultant force acts on the tibial plateau. The purpose of the operation is to reconstruct the normal force condition of the joint and stabilize the knee joint.
The surgical options for anterior cruciate ligament rupture are:
1.Extravasal fixation, although many pet owners are satisfied with the treatment effect, but in strict observation, animals appear obvious degenerative joint lesions, drawer phenomenon still appears at some extension angles, joint instability will still occur.
| Extravasal fixation | ||
 |
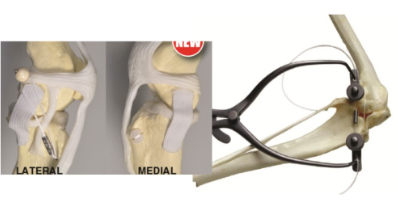 |
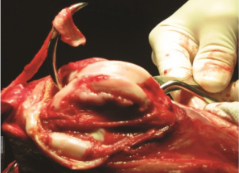 |
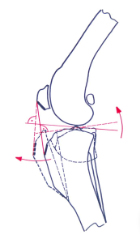
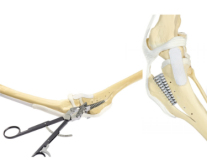
2.TTA (Tibial Tuberosity Advancement), knee straight ligament tension instead of the anterior cruciate ligament. The advantage is that it does not significantly change the joint force situation, requires no drilling and destruction of the tibial tuberosity, curved incision, incomplete osteotomy, but requires special tools.
| TTA (Tibial Tuberosity Advancement) | |||
 |
 |
 |
 |
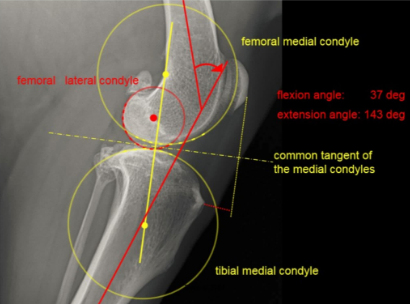
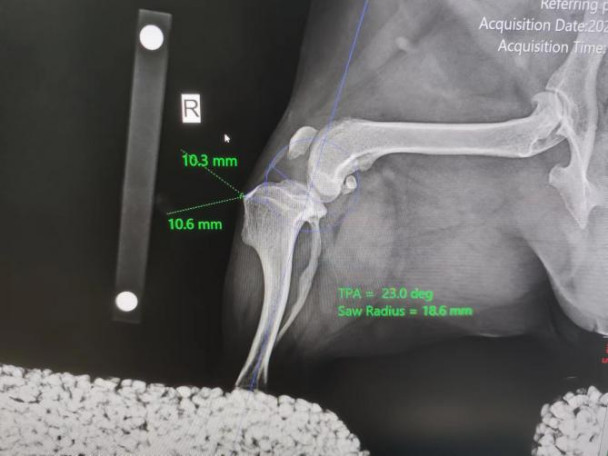
The calculation of the TTA implant box, Common Tangent, projects the circular shape on the femoral condyle with a circular tool, which must be highly consistent with the femoral condyle. If the two femoral condyles are not highly overlapping, draw 2 circles and find the midpoint of 2 circles, use the circular tool and place the circular tool over the tibial condyle to match the circle to the tibial platform. Draw a line a at the center of the femoral condyle and the tibial condyle, and draw a line perpendicular to the line a between the two condyles, which is the common tangent line b that we need. Draw a line c on the head of the straight ligament perpendicular to the common tangent b of the knee and intersect it. Draw a line at the starting point of the tibial protuberance perpendicular to the line c just drawn. Measure the length of the line c. This is the length of the tibial advance that we need. If the cage size is between this length, try to choose large cages.
| Calculation of the TTA implant box | |
 |
 |
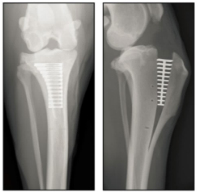
3. The goal of TPLO (Tibial plateau leveling osteotomy, TPLO) TPLO is to offset the anterior tibial tuberosity and maintain the relative position of the tibia and femur. It is effective and persistent, weight-bearing joints and can reduce and prevent the development of arthritis.(Slocum,etal,vet.cl.1993)Clinically, TPLO has rapid postoperative recovery, lower arthritis, better leg weight bearing, and good recovery of joint swing amplitude. Complications were 3% infection, neoplastic lesions, inflammation of the straight knee ligament, 5% secondary surgery, bone nonunion and secondary fractures.
TPLO VS TTA: Both TPLO and TTA can stabilize the knee joint. When the knee is bent, TPLO reduces the force surface of the meniscus, TPLO may overcorrect the joint Angle, TPLO increases the joint force, TTA reduces the joint force, TTA is easier to do, less invasive, TTA recovers faster, but the implant is more expensive.
After communicating with the owner about JOJO, we decided to perform TPLO surgery the next day and add laser physiotherapy to promote postoperative recovery.
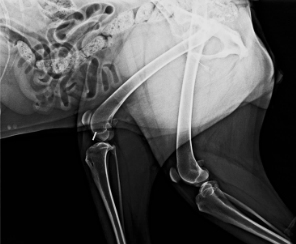
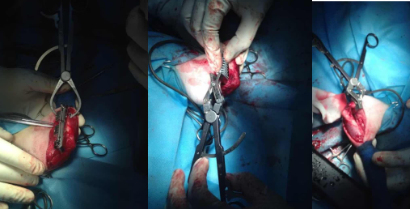
| Picture of the TPLO surgical procedure | |
 |
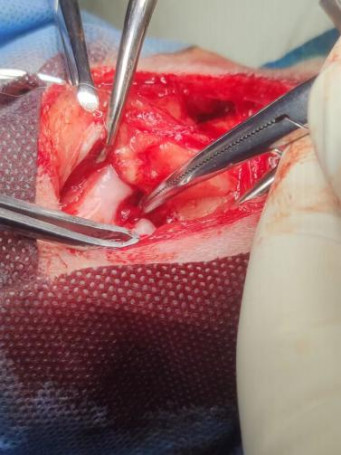 |
 |
|
4.1 Intraoperative laser physiotherapy
The advantages of intraoperative laser use are as follows:
Faster healing: When tissue trauma is formed and laser treatment occurs immediately before wound closure, PBM reduces the release of cytokines, reduces the activity of inflammatory cells, and promotes faster tissue healing.
Treatment is more accurate: intraoperative laser therapy can be targeted to the local area we want to treat, because the laser energy can be irradiated directly into deeper tissue, preventing the laser energy from being absorbed by lighter tissue.
Safe and sterile: During intraoperative laser treatment, the target tissue is clearly visible and no contact with other tissues is required, greatly reducing the risk of postoperative infection.
The intraoperative precautions for laser use are as follows:
Ensure sterility: The laser treatment handle should be disinfected to ensure a sterile environment during the procedure.
Cooperation: the laser therapist and the surgeon must coordinate, and the laser therapist must ensure that the laser treatment handle and fiber cable do not contact the tissue.
Dose adjustment: During intraoperative laser therapy, the tissue targeted is usually more sensitive and the tissue area treated is relatively small, so the dose needs to be adjusted to achieve optimal treatment results.