
2023-07-17 2326
1.Case presentation
1.1 Pet information
Name: Niu Niu
Weight: 6.8 kg
Variety: dog
Age: 10 years old
Gender: female (already sterilized)
1.2 Disease condition
It began on February 20,2022, initially was a common cold, but turned to pneumonia due to improper treatment. On April 20, we came to our hospital for treatment and adopted the Chinese veterinary program to treat pneumonia. During the treatment, the pneumonia was effectively controlled, but a blood clot erupted on April 25.
2.1 Clinical examination
Middle veterinary examination: hindlimb weakness, can not stand, palpation pain, cold hindlimb, femoral artery without pulse, when lying quietly hind limb will flutter. Two eyes are full of red blood silk, blood vessels and anger, red tongue, white moss.
CT examination: abdominal enhancement and plain scan, MIP, MPR and three-dimensional reconstruction, the left axillary artery and lower abdominal aorta were 25.68 long and no enhancement in 33.73mm, respectively, and low density shadow was visible inside, and vascular obstruction was considered.
2.2 Diagnostic results
Blood stasis syndrome, abdominal aortic thrombosis
2.3 Therapeutic regimen
2.3.1 Principle of treatment
Blood stasis is solid when promoting blood circulation to remove blood stasis, long disease more deficiency should replenish qi and nourish blood.
2.3.2 Laser physiotherapy
Laser light can gently promote blood circulation and eliminate congestion.
The general intra-abdominal general symptom pattern was used, and a 25mm probe was used to irradiate the abdominal midline and inguinal sites, with an average power of 6.1W, and each site for 10 minutes, once a day.
2.3.3 Treatment by Chinese herbs
The prescriptions were used: 50g Astragalus mongholicus, 20g Rehmannia glutinosa, 10g Red Paeoniae Trichocarpae, 10g Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge, 10g peachseed, 10g flos carthami, 10g Nutgrass Galingale Rhizome, 10g immature bitter orange, 10g eupolyph, and 1g leeches.
The traditional Chinese medicine was dissolved in 90ml of warm water, 10ml each time, three times a day.
2.4 Therapeutic process
April 25th onset, pet’s hind limb unable to stand
Conduct the laser therapy
May 21, pet can support the stand independently
June 2, pet can walk independently
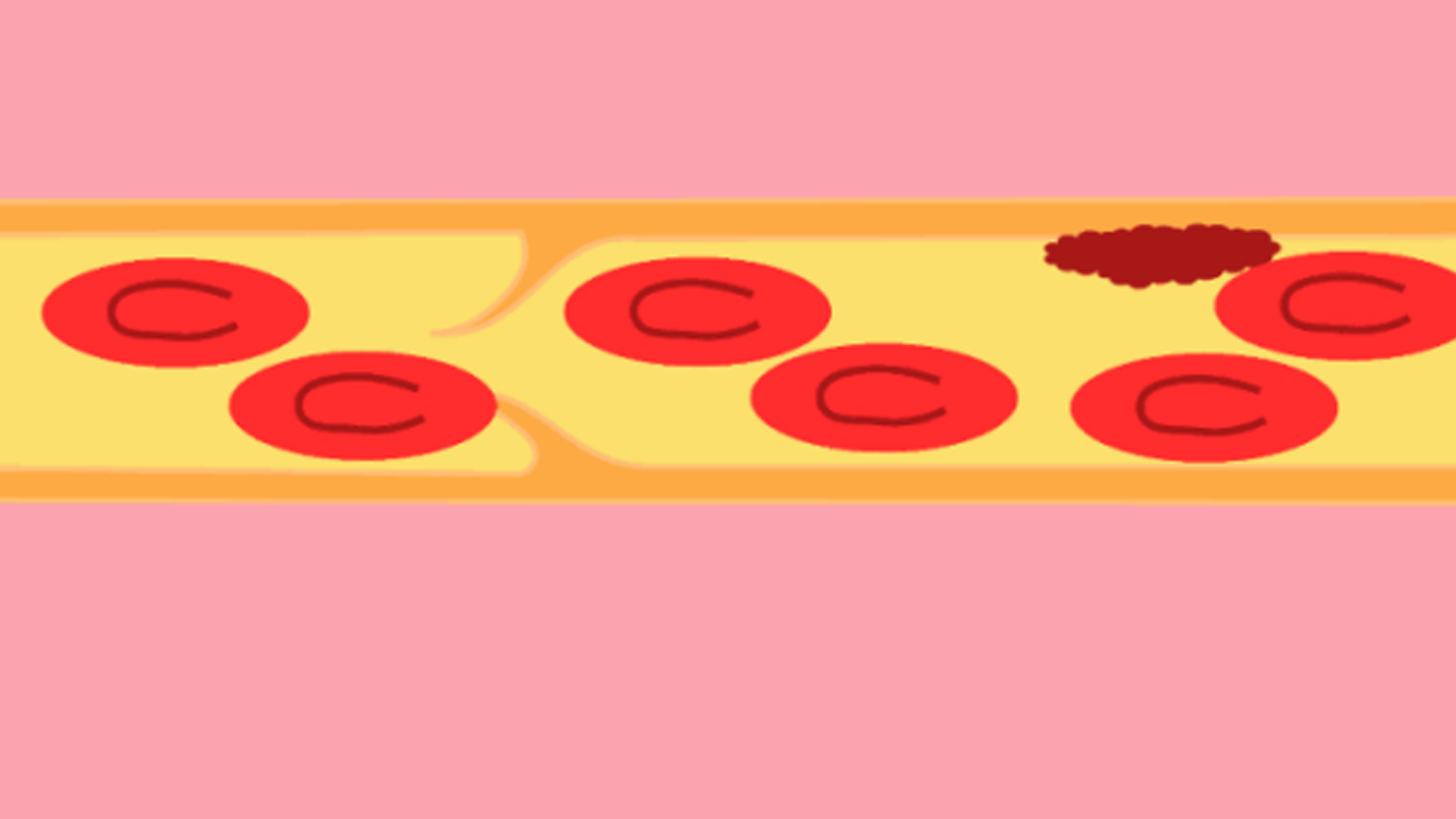
3.1 What is a canine thromboembolic disease?
When the blood is in a state of hypercoagulability, blood stasis or vascular endothelial damage, platelets, fibrin and other blood vessels will agglutinate to form blood clots and flow with the blood, and then block the vascular lumen, which is called thromboembolism.
Deep VTE is not uncommon in human disease but has not been found in small animals; pulmonary embolism is less accurately diagnosed in dogs and cats.
Aortic thromboembolism (ATE) in dogs does not as strongly favor heart disease as in cats, although it is still an underlying cause. Hindlimb paralysis is a persistent acute presentation of thromboembolism in the aorta in dogs; most dogs with ATE experience long-term symptoms of pain, lameness, weakness, and paralysis / paralysis within 2 to 6 months.

Thromboembolism schematic diagram from Wikipedia
3.2 Common treatment methods
Pain relief: The pain should be controlled, preferably with pure opioids, such as methadone.
Supplemental oxygen: hypoxemia should be supplemented with oxygen, or in the form of a nasal oxygen cannula or oxygen cage.
Western medicine treatment: anti-platelet aggregation drugs and therapeutic anticoagulants should be used. The use of fibrinolytic agents is highly controversial because it is associated with very serious side effects.
3.3 Role of laser therapy for aortic thrombosis in dogs
Pain relief: Laser therapy helps animals by regulating the content of serotonin (aka serotonin / 5-HT), stimulating the release of endogenous endorphins and enkephalins, reducing bradykinin and regulating the content of acetylcholine.
Supplemental oxygen: Laser therapy can improve microcirculation, help transport and utilize oxygen molecules, and produce more ATP to help the body quickly obtain the energy needed to return to normal function.
Regulatory cytokines: When endotoxins or inflammatory mediators induce increased expression of tissue factor (TF) in endothelial cells, macrophages, and cell-derived microparticles, excessive activation of coagulation factors occurs, thus keeping the blood in a hypercoagulable state. Laser therapy can regulate proinflammatory factors such as macrophages and help coagulation factors return to a normal state.
Role of traditional Chinese medicine in treating aortic thrombosis in dogs
When thrombosis occurs, it will be accompanied by pain symptoms, caused by poor blood flow. At this point, the use of laser therapy can be through the skin into the body to dredge stasis, to achieve the purpose of relieving pain. At the same time, the use of traditional Chinese medicine to promote blood circulation and remove blood stasis, can further resolve thrombosis and dredge blood vessels.
The dog is obese, with phlegm and dampness, causing spleen deficiency and weakness, easy to get sick. Although the pneumonia condition was effectively controlled a few days before coming to our hospital, the condition delayed for too long, and the blood stasis, which made the abdominal aorta and other blood vessels blocked, and the condition was serious. At this time, the use of laser therapy can use the transmission ability of light waves to go deep into the tissue, which can enhance the metabolism of the local tissue environment, promote the operation of blood flow, and reduce the adverse reactions brought by thrombosis. Subsequently, traditional Chinese medicine was used to adjust the internal tissue function of the body, peach kernel, safflower and Salvia miltiorrhiza were used to promote blood circulation and remove blood stasis, and astragalus was used to replenish qi and promote blood circulation, which greatly enhanced the effect of removing blood stasis.
Good care is the most important thing when dealing with these patients. All risk factors for further thromboembolism should be considered (e. g., catheter, venipuncture site, supine position), and nursing interventions such as reducing venous stasis, such as standing exercise, limb massage, and regular flipped decubitus patients, are also important.